Summary of Publications in 2019
We published 10 papers in the past year; we are looking forward to the coming new year.
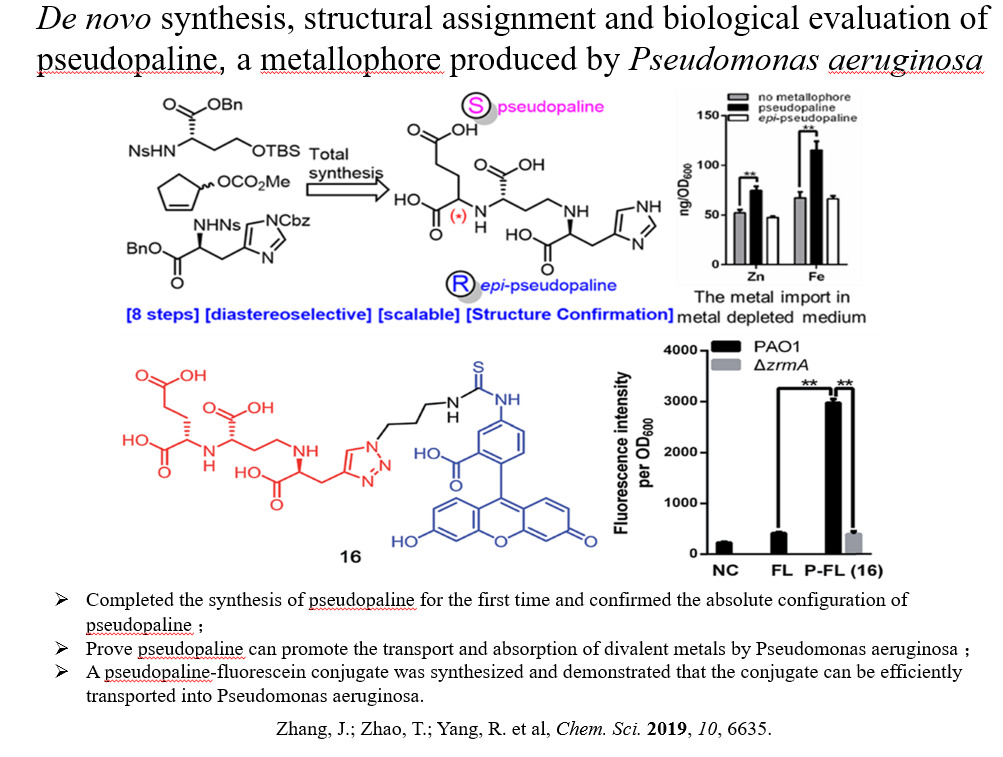 |
|
|
|
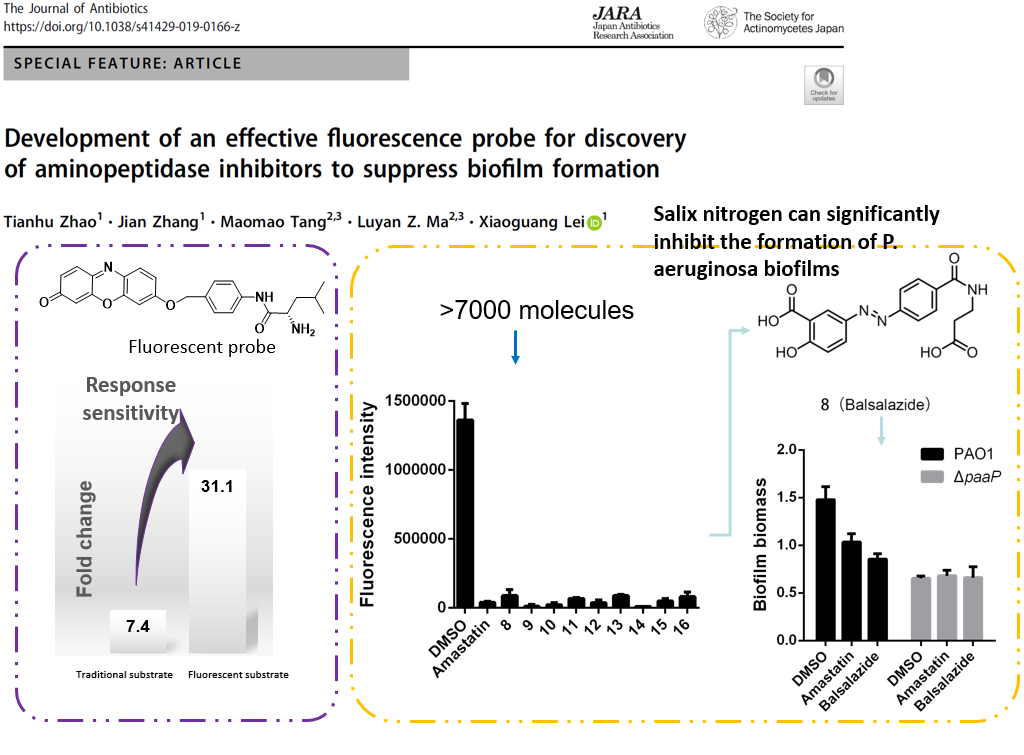
Pseudomonas aeruginosa aminopeptidase plays an important role in biofilm formation and is a potential target for the prevention and treatment of P. aeruginosa infection. Traditionally, L-Leu-p-nitroanilide was used as the substrate for aminopeptidase activity, which was not sensitive enough. The L-leucine was linked to an oxazolone-based "on-off" fluorescent probe to synthesize a fluorescent probe for detecting aminopeptidase activity. The signal intensity change before and after the reaction with the fluorescent probe is up to 31 times, which is significantly better than traditional substrates, and can meet the needs of high-throughput screening. Using this fluorescent probe, nine new aminopeptidase inhibitors were screened from more than 7,000 small molecules. Among them, balsalazide can not only inhibit aminopeptidase activity, but also exhibit good biofilm inhibition ability. Since balsalazide is a marketed drug, its safety has been verified. In the future, it can be used in combination with antibiotics to explore more efficient ways to control P. aeruginosa biofilms. |
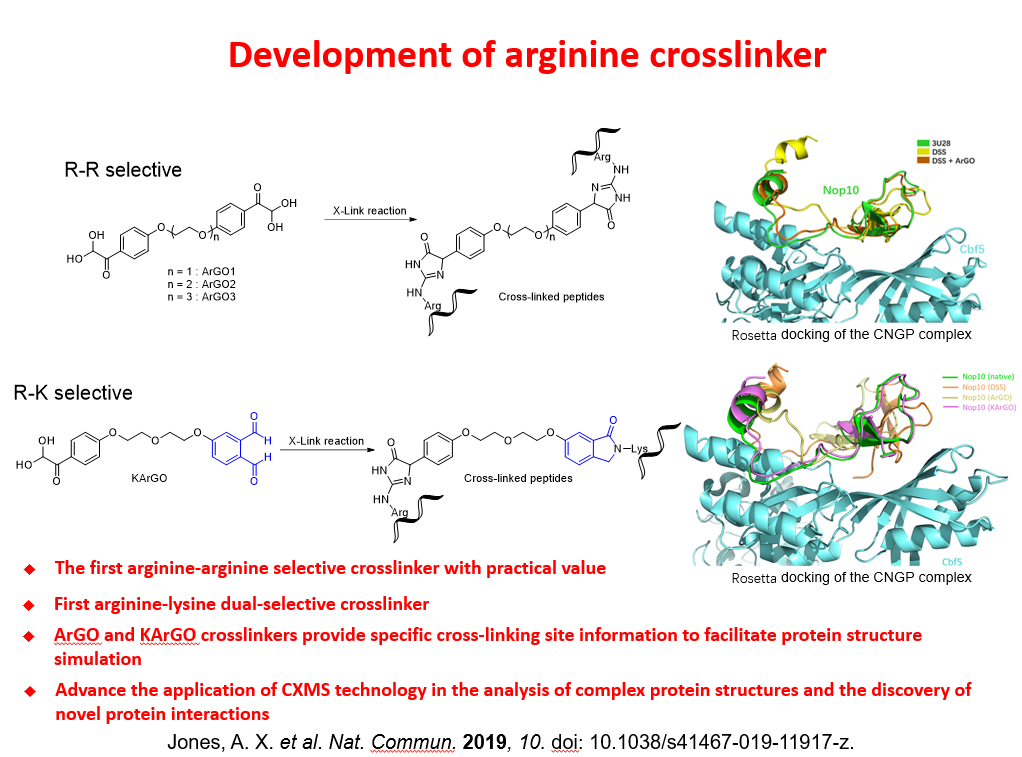 |
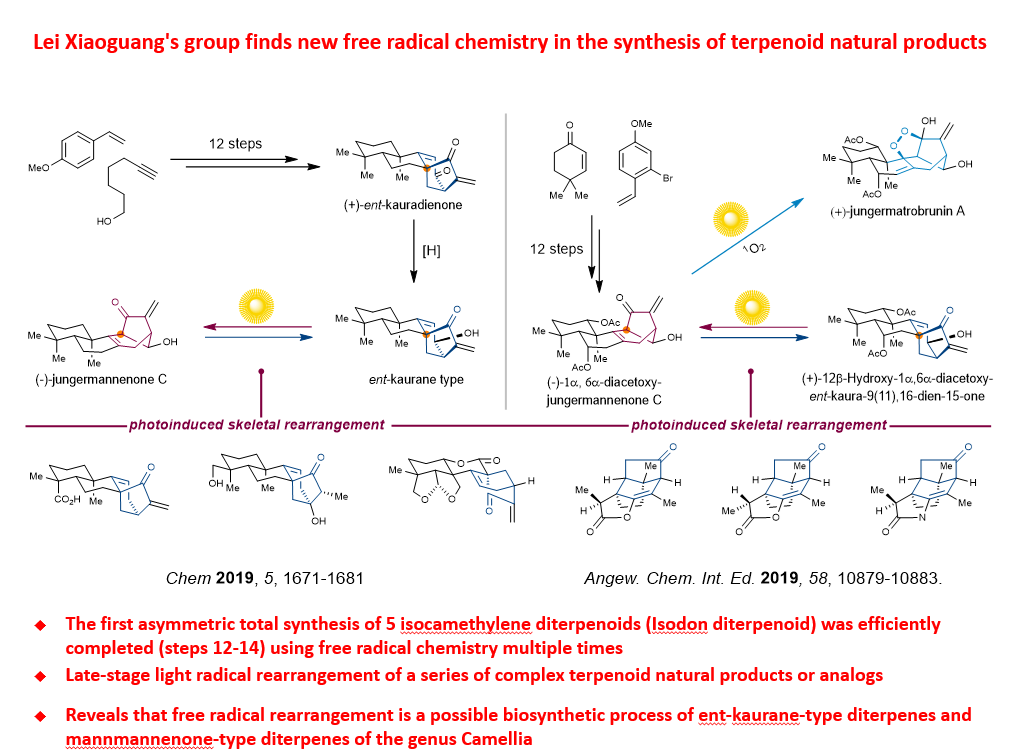 |
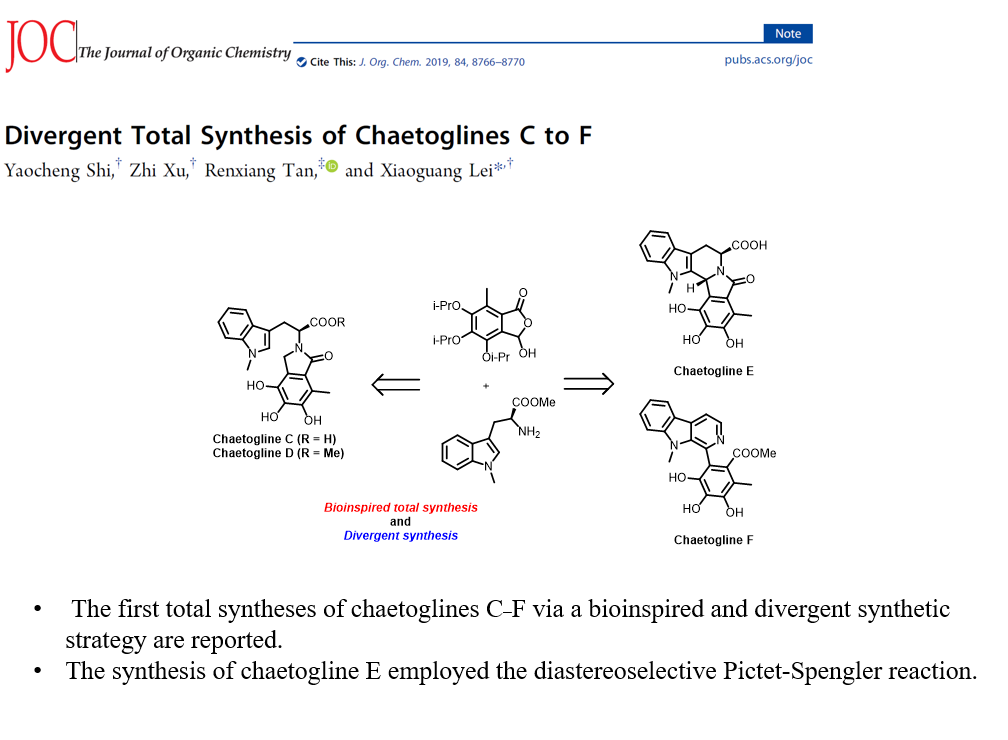 |
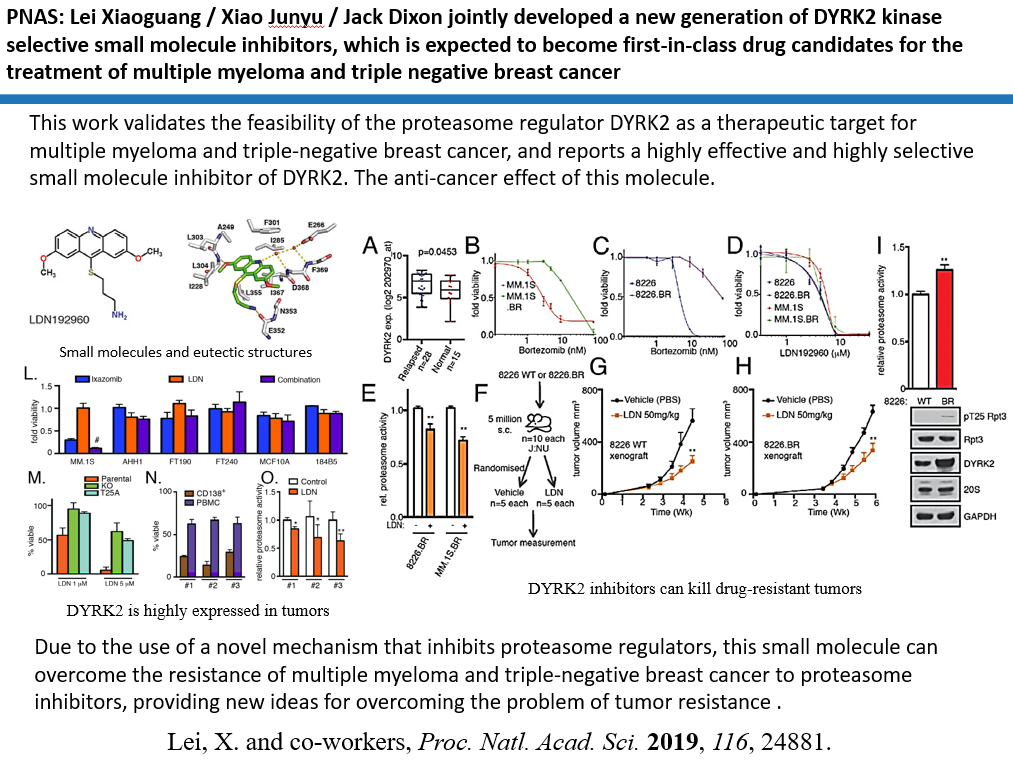 |
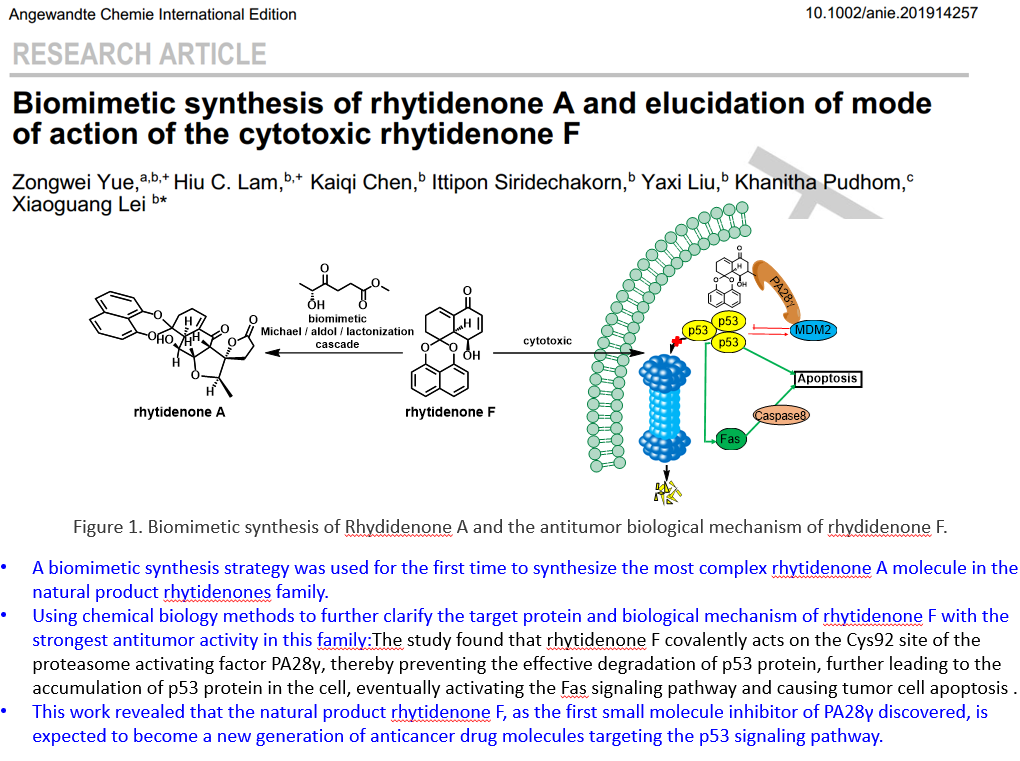 |