Concise and Modular Chemoenzymatic Total Synthesis of Bisbenzylisoquinoline Alkaloids
Jin Wang, Jianxiong Zhao, Zhenyang Yu,
Siyuan Wang, Fusheng Guo, Jun Yang, Lei Gao, Xiaoguang Lei*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202414340
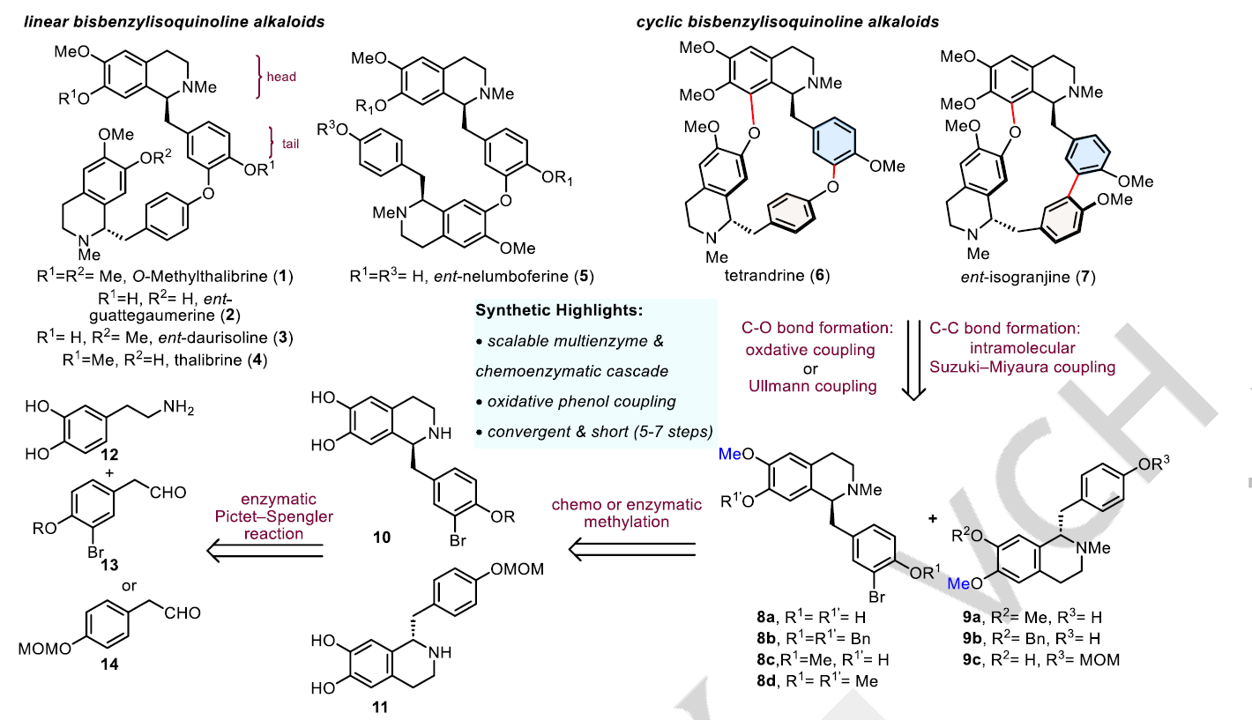
The bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids (bisBIAs) have attracted tremendous attention from the synthetic community due to their diverse and intriguing biological activities. Herein, we report the convergent and modular chemoenzymatic syntheses of eight bisBIAs bearing various substitutes and linkages in 5-7 steps. The gram-scale synthesis of various well-designed enantiopure benzylisoquinoline monomers was accomplished via an enzymatic stereoselective Pictet–Spengler reaction, followed by regioselective enzymatic methylation or chemical functionalizations in a sequential one-pot process. A modified intermolecular copper-mediated Ullmann coupling enabled the concise and efficient total synthesis of five different linear bisBIAs with either head-to-tail or tail-to-tail linkage. A biomimetic oxidative phenol dimerization selectively formed the sterically hindered, electron-rich diaryl ether bond, and subsequent intramolecular Suzuki–Miyaura domino reaction or Ullmann coupling facilitated the first enantioselective total synthesis of three macrocyclic bisBIAs, including ent-isogranjine, tetrandrine and O-methylrepandine. This study highlights the great potential of chemoenzymatic strategies in the total synthesis of diverse bisBIAs and paves the way to further explore the biological functions of these natural products.